Answer:
The second projectile is
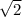 times faster than the first projectile.
times faster than the first projectile.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of first projectile = m
height
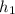 = 2.6 cm
= 2.6 cm
Height
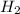 = 5.2 cm
= 5.2 cm
Let velocity of first projectile = V
Velocity of first projectile = V'
From conservation of momentum principal
m V = (m + m) V'
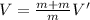
V' =
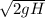
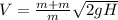
Therefore velocity is directly proportional to the height.
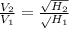
Since
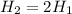
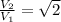
Therefore the second projectile is
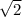 times faster than the first projectile.
times faster than the first projectile.