Answer: a. 7.31 g
b. 20.4 %
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles :
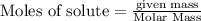
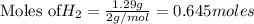
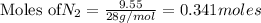
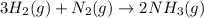
According to stoichiometry :
3 moles of
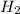 require = 1 mole of
require = 1 mole of
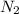
Thus 0.645 moles of
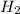 will require=
will require=
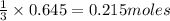 of
of
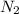
Thus
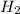 is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
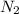 is the excess reagent.
is the excess reagent.
As 3 moles of
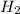 give = 2 moles of
give = 2 moles of
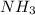
Thus 0.645 moles of
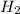 give =
give =
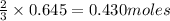 of
of
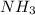
Mass of
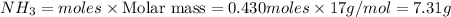
Thus theoretical yield for this reaction under the given conditions is 7.31 g.
b)
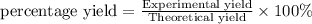
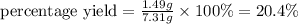
The percent yield for this reaction under the given conditions is 20.4 %