Answer : The partial pressure of
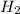 at equilibrium is, 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
at equilibrium is, 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
Explanation :
The partial pressure of
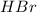 =
=
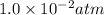
The partial pressure of
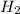 =
=
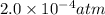
The partial pressure of
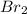 =
=
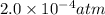
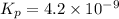
The balanced equilibrium reaction is,
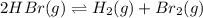
Initial pressure 1.0×10⁻² 2.0×10⁻⁴ 2.0×10⁻⁴
At eqm. (1.0×10⁻²-2p) (2.0×10⁻⁴+p) (2.0×10⁻⁴+p)
The expression of equilibrium constant
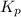 for the reaction will be:
for the reaction will be:
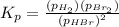
Now put all the values in this expression, we get :
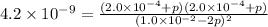
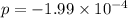
The partial pressure of
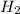 at equilibrium = (2.0×10⁻⁴+(-1.99×10⁻⁴) )= 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
at equilibrium = (2.0×10⁻⁴+(-1.99×10⁻⁴) )= 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
Therefore, the partial pressure of
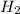 at equilibrium is, 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
at equilibrium is, 1.0 × 10⁻⁶