Answer:
27.16 lb/in²
Step-by-step explanation:
initial temperature, T1 = 3.4 °C = 276.4 K
initial gauge pressure, P1 = 24 lb/in²
atmospheric pressure, Po = 14.7 lb/in²
initial absolute pressure, P1' = Po + P1 = 14.7 + 24 = 38.7 lb/in²
final temperature, T2 = 26 °C = 299 K
Let the final gauge pressure is P2.
use the ideal gas equation and the volume is constant.
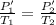
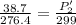
P2' = 41.86 lb/in²
Now the gauge pressure, P2 = P2' - Po = 41.86 - 14.7 = 27.16 lb/in²
Thus, the new gauge pressure is 27.16 lb/in².