Answer:
Required average rate of change over the interval [1.9, 2] is 5.9, [1.99, 2] is 5.99, [2, 2.1] is 6.1, [2, 2.01] is 6.01 and the instantaneous change at x=2 is 6.
Explanation:
Given function is,
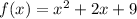
To find the avarage rate of change over given intervals. We know from Lagranges Mean value theorem, the average rate of change of a function F(x) over a interval
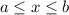 is,
is,
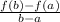 .
.
(a) On the interval,
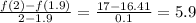
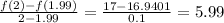
(b) On the interval,
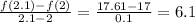
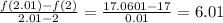
(c) Instantaneous rate of change at x=2 is,
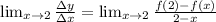
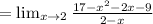
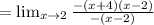

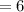
Hence the results.