Answer:
A) the probability that a randomly selected score is greater than 29 points is 0.1587
B) The percentage of students scores are between 31 and 23 is 95.44%
C) A student who scores 31 is in the 97.72% percentile
Explanation:
ACT mathematics score for a particular year are normally distributed with a mean of 27 and a standard deviation of 2 points.
Part A: What is the probability that a randomly selected score is greater than 29 points?
Part B: What percentage of students scores are between 31 and 23?
Part C: A student who scores 31 is in the ______ percentile.
A) Given that:
Mean (m) = 27 and standard deviation (s) = 2 points
Since the ACT mathematics score is normally distributed, we can use z score. To calculate Z score we use the equation:
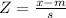
substituting values:
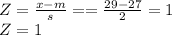
P(X > 29) = P(Z > 1) = 1 - P(Z<1)
Using Z tables
P(X > 29) = P(Z > 1) = 1 - P(Z<1) = 1 - 0.8413 = 0.1587 = 15.87%
P(X > 29) = 0.1587
the probability that a randomly selected score is greater than 29 points is 0.1587
B) For score of 31
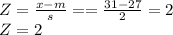
For score of 23
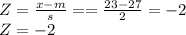
P(23 < X < 31) = P(-2 < Z < 2) = P(Z < 2) - P(Z < -2) = 0.9772 - 0.0228 = 0.9544
P(23 < X < 31) = 0.9544 = 95.44%
The percentage of students scores are between 31 and 23 is 95.44%
C) For score of 31
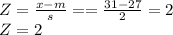
P(X < 31) = P(Z < 2) = 0.9772 = 97.72%
A student who scores 31 is in the 97.72% percentile