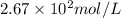This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
The Henry's law constant for oxygen dissolved in water is 4.34 × 10⁹ g/L.Pa at 25⁰C.If the partial pressure of oxygen in air is 0.2 atm, under atmospheric conditions, calculate the molar concentration of oxygen in air-saturated and oxygen saturated water.
Answer : The molar concentration of oxygen is,
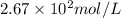
Explanation :
As we know that,
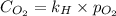
where,
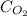 = molar solubility of
= molar solubility of
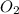 = ?
= ?
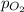 = partial pressure of
= partial pressure of
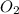 = 0.2 atm = 1.97×10⁻⁶ Pa
= 0.2 atm = 1.97×10⁻⁶ Pa
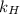 = Henry's law constant = 4.34 × 10⁹ g/L.Pa
= Henry's law constant = 4.34 × 10⁹ g/L.Pa
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
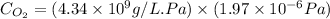
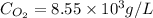
Now we have to molar concentration of oxygen.
Molar concentration of oxygen =
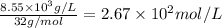
Therefore, the molar concentration of oxygen is,