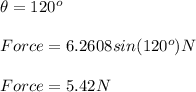Question:
A wire 2.80 m in length carries a current of 5.20 A in a region where a uniform magnetic field has a magnitude of 0.430 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming the following angles between the magnetic field and the current.
(a)60 (b)90 (c)120
Answer:
(a)5.42 N (b)6.26 N (c)5.42 N
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question
Length of wire (L) = 2.80 m
Current in wire (I) = 5.20 A
Magnetic field (B) = 0.430 T
Angle are different in each part.
The magnetic force is given by
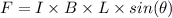
So from data
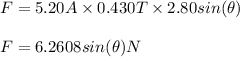
Now sub parts
(a)
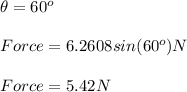
(b)
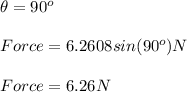
(c)