Answer: The concentrations of A , B , and C at equilibrium are 0.1583 M, 0.2583 M, and 0.1417 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction equation is as follows.
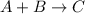
Initial : 0.3 0.4 0
Change: -x -x x
Equilbm: (0.3 - x) (0.4 - x) x
We know that, relation between standard free energy and equilibrium constant is as follows.
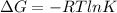
Putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
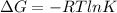
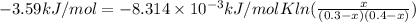
x = 0.1417
Hence, at equilibrium
= 0.1583 M
= 0.2583 M