Answer:
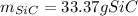
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
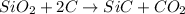
Thus, by stoichiometry, the limiting reagent is computed by comparing the available moles of silicon dioxide and the consumed moles of silicon dioxide by graphite as shown below:
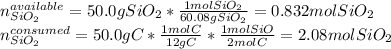
In such a way, since there will be less available silicon dioxide, it is the limiting reagent, therefore, the grams of silicon carbide, turns out:
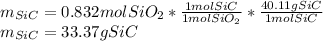
Best regards.