Answer:
pH of the benzoic acid solution = 3.35
Explanation:
Benzoic acid is a weak monoprotic acid
pKa = 4.2
⇒ Ka = 6.3 x 10⁻⁵
C₆H₅COOH ⇄ C₆H₅COO⁻ + H⁺
Initial concentration C molar 0 0
At equilibrium (c - cα) cα cα
Acid dissociation constant Ka =
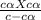
⇒ 6.3 x 10⁻⁵ = α²c ................(1)
(for weak electrolyte 1 -α = 1)
Concentration of benzoic acid C = 25 x 0.126 x 10⁻³ = 0.00315 molar
From eqn (1)
α² =
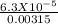
⇒ α = √(
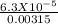 )
)
⇒ α = 0.14
So concentration of H⁺ ion = 0.14 x 0.00315 = 0.000441
pH = - log 0.000441 = 3.35
We not considered H⁺ concentration of water because pH < 7