Answer:
Explanation:
General form of the linear differential equation can be written as:
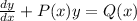
For this case, we can rewrite the equation as:
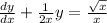
Here
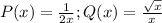
To find the solution (y(x)), we can use the integration factor method:
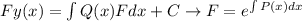
Then
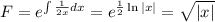
So, we can find:
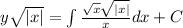
Suppose that
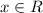 , then
, then
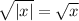 , and we find:
, and we find:
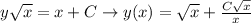
To check our solution is right or not, put your y(x) back to the ODE:
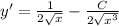
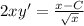
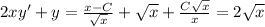
(it means your solution is right)