This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
The equilibrium constant is equal to 5.00 at 1300 K for the reaction:
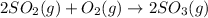
If initial concentrations are [SO₂] = 1.20 M, [O₂] = 0.45 M, and [SO₃] = 1.80 M, the system is
A) at equilibrium.
B) not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.
C) not at equilibrium and will shift to the left to achieve an equilibrium state.
D) not at equilibrium and will shift to the right to achieve an equilibrium state.
Answer : The correct option is, (A) at equilibrium.
Explanation :
Reaction quotient (Q) : It is defined as the measurement of the relative amounts of products and reactants present during a reaction at a particular time.
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
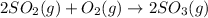
The expression for reaction quotient will be :
![Q=([SO_3]^2)/([SO_2]^2[O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bklldfmk226zmpz2o9jptt80pjo0lutelr.png)
In this expression, only gaseous or aqueous states are includes and pure liquid or solid states are omitted.
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get
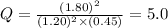
The given equilibrium constant value is,
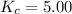
Equilibrium constant : It is defined as the equilibrium constant. It is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants.
There are 3 conditions:
When
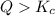 that means product > reactant. So, the reaction is reactant favored.
that means product > reactant. So, the reaction is reactant favored.
When
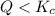 that means reactant > product. So, the reaction is product favored.
that means reactant > product. So, the reaction is product favored.
When
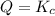 that means product = reactant. So, the reaction is in equilibrium.
that means product = reactant. So, the reaction is in equilibrium.
From the above we conclude that, the
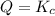 that means product = reactant. So, the reaction is in equilibrium.
that means product = reactant. So, the reaction is in equilibrium.
Hence, the correct option is, (A) at equilibrium.