Answer:
a) Exponential decay
b,) The parent function is shifted up 1 unit.
Explanation:
Assuming your function is
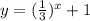
Then we can compare this to:
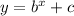
If
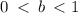
then y is an exponential decay function.
If |b|>1, then y is an exponential growth.
We can see that:
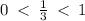
Therefore the given function is an exponential decay.
The parent function is shifted up 1 unit.