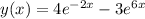Answer:
The initial value problem
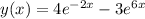
Explanation:
Step1:-
a) Given second order homogenous constant co-efficient equation
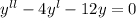
Given equation in the operator form is
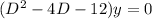
Step 2:-
b) Let f(D) =
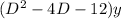
Then the auxiliary equation is
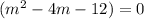
Find the factors of the auxiliary equation is
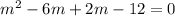
m(m-6) + 2(m-6) =0
m+2 =0 and m-6=0
m=-2 and m=6
The roots are real and different
The general solution
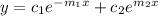
the roots are
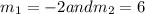
The general solution of given differential equation is
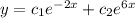
Step 3:-
C) Given initial conditions are y(0) =1 and y1 (0) =-26
The general solution of given differential equation is
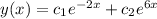 .....(1)
.....(1)
substitute x =0 and y(0) =1
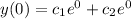
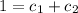 .........(2)
.........(2)
Differentiating equation (1) with respective to 'x'
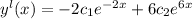
substitute x= o and y1 (0) =-26
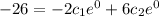
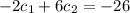 .............(3)
.............(3)
solving (2) and (3) by using substitution method
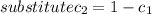 in equation (3)
in equation (3)
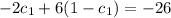
on simplification , we get

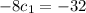
dividing by'8' we get
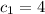
substitute
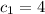 in equation
in equation
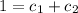
so

now substitute
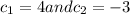 in general solution
in general solution
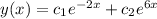
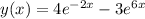
now the initial value problem