The given question is incomplete. The complete question is as follows.
Nitric acid is a key industrial chemical, largely used to make fertilizers and explosives. The first step in its synthesis is the oxidation of ammonia. In this reaction, gaseous ammonia reacts with dioxygen gas to produce nitrogen monoxide gas and water.
Suppose a chemical engineer studying a new catalyst for the oxidation of ammonia reaction finds that 645. liters per second of dioxygen are consumed when the reaction is run at 195.oC and 0.88 atm. Calculate the rate at which nitrogen monoxide is being produced. Give your answer in kilograms per second. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.
Step-by-step explanation:
Chemical equation for the oxidation of ammonia is as follows.
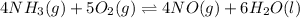
Then volume of
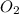 per second consumed is as follows.
per second consumed is as follows.
V =
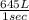
As this reaction is taking place at a temperature of
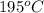 (468.15 K) and pressure 0.88 atm. Hence, moles of consumption of
(468.15 K) and pressure 0.88 atm. Hence, moles of consumption of
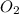 are calculated as follows.
are calculated as follows.
n =
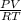
=
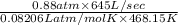
= 14.77 mol
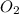 /sec
/sec
When 5 moles of
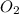 produces 4 moles of NO then the amount of NO produced from 14.77 mol
produces 4 moles of NO then the amount of NO produced from 14.77 mol
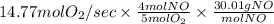
= 354.60 g/s
Therefore, NO formed per second is as follows.
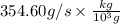
= 0.35 kg/s
Thus, we can conclude that the rate at which nitrogen monoxide is being produced is 0.35 kg/s.