The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
Consider the following chemical equilibrium: 2PbO + O₂= 2PbO₂
Now write an equation below that shows how to calculate
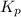 from
from
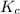 for this reaction at an absolute temperature T.
for this reaction at an absolute temperature T.
You can assume is comfortably above room temperature. If you include any common physical constants in your equation be sure you use their standard symbols, found in the ALEKS Calculator.
Answer: The expression of
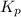 from
from
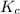 for given equation is written below.
for given equation is written below.
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical equation:
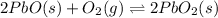
The expression of
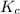 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=(1)/([O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6ftfm1o5jlz6of1ao2l1zuc5wzf8ixie7w.png)
The concentration of pure liquids and solids are taken as 1 in equilibrium constant expression. So, the concentration of lead (II) oxide and lead (IV) oxide do not appear in the expression.
Relation of
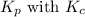 is given by the formula:
is given by the formula:
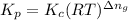
Where,
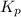 = equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure
= equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure
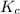 = equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
= equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
R = Gas constant =
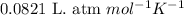
T = absolute temperature = T
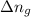 = change in number of moles of gas particles =
= change in number of moles of gas particles =
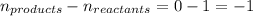
Putting values in above equation, we get:
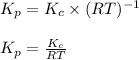
Hence, the expression of
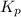 from
from
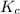 for given equation is written above.
for given equation is written above.