Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
11 oscillations in 18.2 s
Time period is defined as the time taken to complete one oscillation.
T = 18.2 / 11 = 1.655 s
mass, m = 290 g = 0.29 kg
Δx = 21.1 cm = 0.211 m
ω = 2π / T = (2 x 3.14) / 1.655 = 3.796 rad/s
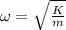
Where, K is the spring constant
K = ω² m = 3.796 x 3.796 x 0.29 = 4.18 N/m
Now, mg = K Δx
0.29 x g = 4.18 x 0.211
g = 3.04 m/s²