Answer:
7.79 moles
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the mass of helium gas = Mass of argon gas = x g
Moles of helium =
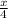 moles
moles
Moles of argon =
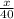 moles
moles
Total moles =
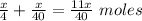
Given that:
Temperature = 398 K
V = 80.0 L
Pressure = 3.50 atm
Using ideal gas equation as:
PV=nRT
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.0821 L atm/ K mol
Applying the equation as:
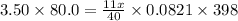
x=31.16 g
Moles of helium = 31.16 / 4 = 7.79 moles