To solve this problem we will apply the concepts related to the Friction force and work. The friction force can be defined as the product between the Normal Force (Mass by gravity) and the dynamic friction constant. In the case of Work this is defined as the product of the distance traveled by the applied force. Then we will solve the points sequentially to find the answer to each point,
PART A) The friction force with the given data is,
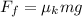
Here,
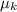 = Kinetic coefficient
= Kinetic coefficient
m = Mass
g = Gravitational acceleration
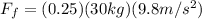
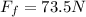
PART B) The work done by the worker is the distance traveled for the previously force found, then
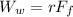
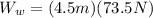
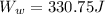
PART C) The work done by the friction force would be the distance traveled with the previously calculated force, therefore
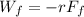
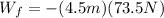
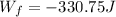
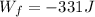
PART D) The work done by the normal force is,
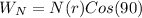
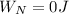
The work done by gravitational force is
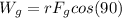
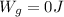
PART E) The expression for the total work done is,
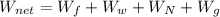
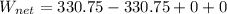
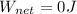
Therefore the net work done by the system is 0J