Answer:
Current ratio- 2.03 2.33 1.73 and Acid-test ratio- 0.98 0.43 0.60
Step-by-step explanation:
Attach is the table of given cases
Acid test ratio=
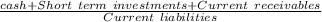
Now, solving for acid test ratio.
Case x
⇒ Acid test ratio=
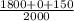
⇒ Acid test ratio=
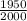
∴ Acid test ratio=
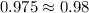
Case y
⇒ Acid test ratio=
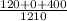
⇒ Acid test ratio=
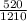
∴ Acid test ratio=
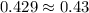
Case Z
⇒ Acid test ratio=
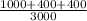
⇒ Acid test ratio=
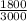
∴ Acid test ratio=
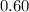
Next solving for current ratio.
We know, current ratio=
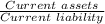
Case x
⇒ current ratio=
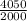
∴ current ratio=
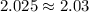
Case y
⇒ current ratio=
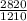
∴ current ratio=
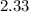
Case Z
⇒ current ratio=
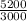
∴ current ratio=
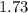
Hence, Current ratio- 2.03 2.33 1.73 and Acid-test ratio- 0.98 0.43 0.60