Answer:
2.58 kPa
Explanation:
Initial Pressure of the nitrogen gas = 6.85 kPa
Initial temperature of the nitrogen gas 539 K
Final Pressure of the nitrogen gas = ???
Final Pressure of the nitrogen gas = -62°C = (273+(-62))K
= 211 K
∴ The equation that can be used to approach this question relating to pressure and temperature at a fixed constant volume is Gay-Lussac's Law of Combine Volume. The expression for Gay-Lussac's Law is given as:
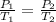
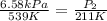
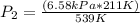
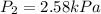
Thus, the pressure will be 2.58 kPa at -62°C