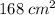Answer:
The maximum error in calculating the surface area of the box is
Explanation:
The differential df of a function
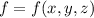 is related to the differentials dx, dy, and dz by
is related to the differentials dx, dy, and dz by
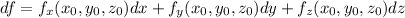
We can use this relationship to approximate small changes in f that result from small changes in x, y and z.
Let the dimensions of the box be
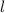 ,
,
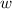 , and
, and
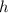 for length, width, and height, respectively.
for length, width, and height, respectively.
The surface area of a box is the total area of each side and is given by
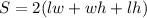
The change in area can be written as:
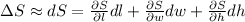
From the information given the partial derivatives are evaluated at
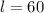 ,
,
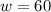 , and
, and
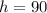 , and
, and
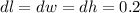 .
.
The partial derivatives are
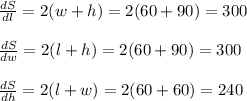
Substituting these in for
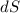 ,
,
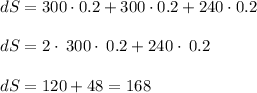
Thus, the maximum error in calculating the surface area of the box is