Answer:
The answer to the question is;
The pH of a solution containing an amphetamine (with pKb of 4.2) concentration of 205 mg/l is 10.4.
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve the question we note that the
The mass of amphetamine = 205 mg/l
The molar mass of amphetamine = 135.2062 g/mol
Number of moles of amphetamine = (205 mg)/(135.2062 g/mol) = 1.5×10⁻³ moles
That is the initial concentration of amphetamine = 1.5×10⁻³ M
We have
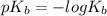 therefore
therefore
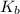 =
=
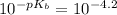 = 6.3×10⁻⁵
= 6.3×10⁻⁵
Then
![K_b=([C_9H_(14)N][OH^-])/([C_9H_(13)N])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/jjijsgi4up9croz5womh9i8bdfp110z1rh.png) = 6.3×10⁻⁵
= 6.3×10⁻⁵
Which gives 6.3×10⁻⁵ =
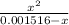
Solving, we get
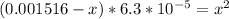
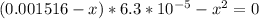
From which by factorizing gives (x+3.42×10⁻⁴)×(x-2.79×10⁻⁴) = 0
That is x = -3.42×10⁻⁴ or 2.79×10⁻⁴ which gives x= 2.79×10⁻⁴ since we are dealing with concentration
However x = [OH⁻] = 2.79×10⁻⁴
pOH = -log[OH⁻] = -log(2.79×10⁻⁴) = 3.5538
pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 3.5538 = 10.446 ≈ 10.4
the pH of a solution containing an amphetamine concentration of 205 mg/l = 10.4.