Answer:
See explanation.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello
(a) In this case, one uses the following formulas, which allow to compute the mass fraction of each component:
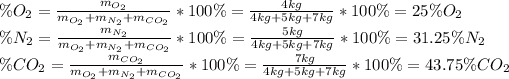
(b) For the mole fractions, it is necessary to find all the components' moles by using their molar mass as shown below:
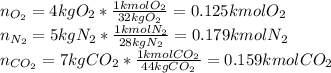
Now, the mole fractions:

(c) Finally the average molar mass is computed considering the molar fractions and each component's molar mass:
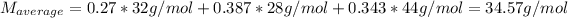
And the gas constant:
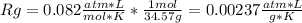
Best regards.