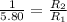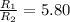Answer:
Ratio of resistance of heater A to resistance of heater B is 5.80
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider C be the specific heat of water, R₁ and R₂ be the resistance of heater A and heater B respectively.
Given:
Mass of water in heater A, m₁ = 1 L
Mass of water in heater B, m₂ = 5.80 L
Initial temperature, T₀ = 20 ⁰C
Final temperature, T₁ = 90 ⁰C
Time, t = 5 min
Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of water by heaters A and B are given by:
Q₁ = m₁C(T₁ - T₀) and
Q₂ = m₂C(T₁ - T₀)
Ratio of power used by both the heaters A and B is:
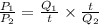
Since, time t, temperature difference(T₁ - T₀) and specific heat C are same for both the heaters A and B. So, the above equation becomes:
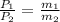 ...(1)
...(1)
The relation to determine electrical power for both heaters A and B are:
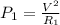 and
and
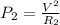
Here V is the voltage applied to both the heaters and is equal.
So, the ratio of electrical power of heaters is:
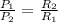 ....(2)
....(2)
But according to the problem, the electrical power is converted into the thermal power. So,equation (1) and (2) are equal. Hence,
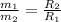
Substitute the suitable values in the above equation.