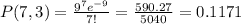Answer:
a)
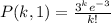
b) E(x)=12
c)
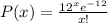
d) 0.2240
e) 0.1144
f) 0.1171
Explanation:
a) The appropiate Poisson probability function (k events in t interval) is:
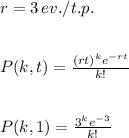
b) In this case, t=4. The expected number of ocurrences is equal to the rate of events multiplied by the time periods:
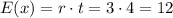
c) Probability function for 4 time periods.
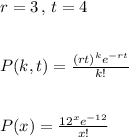
d) Three occurrences in one time period
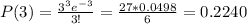
e) Twelve occurrences in four time periods
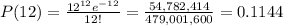
f) Seven events in three time periods