Answer:
a) The rate of reaction increases by factor of 2.
b) The rate of reaction increases by factor of 0.25.
c) The rate of reaction increases by factor of 9.
Step-by-step explanation:
a)
Rate of the reaction ;
![R=k[A]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cmkm27uxrbpkwm6gz5qezjtxb9t3rakbo2.png)
if [A] is doubled, then rate of the reaction = R'
![R'=k[2A]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/pjh5e4x4xwi65eh10x8obicdjaugl56vz7.png)
![R'=2k[A]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bv8629dtjdp17k64syehdf62rmn855cyiy.png)
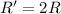
The rate of reaction increases by factor of 2.
b)
Rate of the reaction ;
![R=k[B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yxd64qh72v0635oftkmva03aw7vmyzj8lz.png)
if [B] is halved, then rate of the reaction = R'
![R'=k[(B)/(2)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/26fhar69b15mjm77pwm5xid4gb1sz3mccx.png)
![R'=(1)/(4)k[B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/n425eiebbfepfo7h8nrcoq1s5n66pjojw2.png)
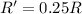
The rate of reaction increases by factor of 0.25.
c)
Rate of the reaction ;
![R=k[C]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g77i8hmk0245ndzbfjlyhmub36nqk25bvc.png)
if [C] is tripled, then rate of the reaction = R'
![R'=k[3C]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cgyfapghfbu3gs7zok9q1e589vabgflwfy.png)
![R'=9k[C]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/r5mgn4va1d5hdnsvwu8qsettleqbxqwj3r.png)
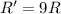
The rate of reaction increases by factor of 9.