Answer: The equilibrium concentration of methane, carbon tetrachloride and
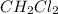 are 0.2686 M, 0.2686 M and 0.0828 M respectively.
are 0.2686 M, 0.2686 M and 0.0828 M respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is calculated by using the equation:
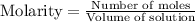
Moles of methane = 0.310 moles
Volume of solution = 1.00 L
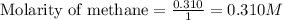
- For carbon tetrachloride:
Moles of carbon tetrachloride = 0.310 moles
Volume of solution = 1.00 L
For the given chemical equation:
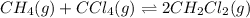
Initial: 0.310 0.310
At eqllm: 0.310-x 0.310-x 2x
The expression of
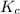 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([CH_2Cl_2]^2)/([CH_4][CCl_4])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1t5ood8uj7lh5fvuf2f84ifflo3fon4yzs.png)
We are given:
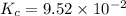
Putting values in above equation, we get:
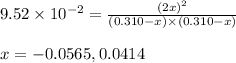
Neglecting the negative value of 'x' because concentration cannot be negative
So, equilibrium concentration of methane = (0.310 - x) = [0.310 - 0.0414] = 0.2686 M
Equilibrium concentration of carbon tetrachloride = (0.310 - x) = [0.310 - 0.0414] = 0.2686 M
Equilibrium concentration of
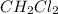 = 2x = (2 × 0.0414) = 0.0828 M
= 2x = (2 × 0.0414) = 0.0828 M
Hence, the equilibrium concentration of methane, carbon tetrachloride and
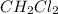 are 0.2686 M, 0.2686 M and 0.0828 M respectively.
are 0.2686 M, 0.2686 M and 0.0828 M respectively.