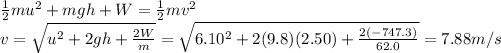b) 747.3 J
a) 7.88 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
b)
We start by solving part b) first.
The internal energy generated when crossing the rough patch is equal (in magnitude) to the work done by the friction force on the skier.
The magnitude of the friction force is:
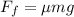
where:
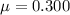 is the coefficient of friction
is the coefficient of friction
m = 62.0 kg is the mass of the skier
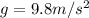 is the acceleration due to gravity
is the acceleration due to gravity
Therefore, the work done by friction is:
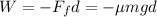
where
d = 4.10 m is the length of the rough patch
The negative sign is due to the fact that the friction force is opposite to the direction of motion of the skier
Substituting,
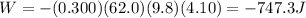
So, the internal energy generated in crossing the rough patch is 747.3 J.
a)
If we take the bottom of the hill as reference level, the initial mechanical energy of the skier is sum of his kinetic energy + potential energy:
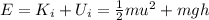
where
m = 62.0 kg is the mass
u = 6.10 m/s is the initial speed
h = 2.50 m is the height of the hill
After crossing the rough patch, the new mechanical energy is
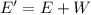
where
W = -747.3 J is the work done by friction
At the bottom of the hill, the final energy is just kinetic energy,
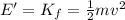
where v is the final speed.
According to the law of conservation of energy, we can write:
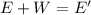
So we find v: