Answer:
-1.5m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider one of the equations of motion as follows;
v² = u² + 2as -------------------------(i)
Where;
v = final velocity of moving body (airplane in this case)
u = initial velocity of the body
a = acceleration of motion of the body
s = distance covered by the body
From the question;
v = 0 [since the airplane comes to a stop]
u = 55m/s
s = 1.00km = 1000m
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
0² = 55² + 2a(1000)
0 = 3025 + 2000a
Collect like terms;
2000a = -3025
Solve for a;
a =
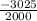
a = -1.5m/s²
Therefore the acceleration that allows the plane to come to a stop in 1.00km is -1.5m/s².
The negative sign shows that the plane is actually decelerating.