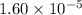Answer : The value of
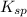 of the generic salt is,
of the generic salt is,
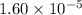
Explanation :
As we are given that, a solubility of salt is, 8.70 g/L that means 8.70 grams of salt present in 1 L of solution.
First we have to calculate the moles of salt
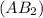
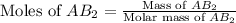
Molar mass of
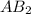 = 345 g/mol
= 345 g/mol
Now we have to calculate the concentration of
The equilibrium chemical reaction will be:
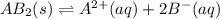
Concentration of
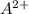 =
=
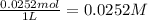
Concentration of
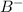 =
=
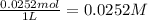
The solubility constant expression for this reaction is:
![K_(sp)=[A^(2+)][B^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4t3yqv8c1g3ygm5mi9148ufqww7ihasr1a.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
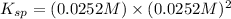
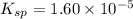
Thus, the value of
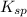 of the generic salt is,
of the generic salt is,