Answer:
The estimation for the slope on this case is
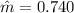
And the associated standard error is
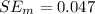
For the critical value we need to find the degrees of freedom given by:
Since we don't have the sample size we can assume it large enough to consider the normal approximation to the t distribution and on this case the critical value for 95% of confidence would be
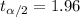
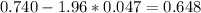
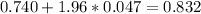
The confidence interval would be between (0.648, 0.832)
Explanation:
We are assuming that the estimation was using the least squares method
For this case we need to calculate the slope with the following formula:
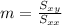
Where:

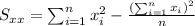
Nowe we can find the means for x and y like this:
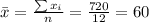
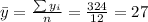
And we can find the intercept using this:
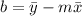
The confidence interval for this case is given by this formula:
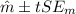
The estimation for the slope on this case is
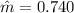
And the associated standard error is
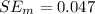
For the critical value we need to find the degrees of freedom given by:
Since we don't have the sample size we can assume it large enough to consider the normal approximation to the t distribution and on this case the critical value for 95% of confidence would be
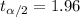
And replacing we got:
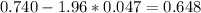
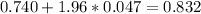
The confidence interval would be between (0.648, 0.832)