Answer:
t = 22.32 s
Step-by-step explanation:
The kinetics of a reaction can be known graphically by plotting the concentration vs time experimental data on a sheet of graph.
- The concentration vs time graph of zero order reactions is linear with negative slope.
- The concentration vs time graph for a first order reactions is a exponential curve. For first order kinetics the graph between the natural logarithm of the concentration vs time comes out to be a straight graph with negative slope.
- The concentration vs time graph for a second order reaction is a hyperbolic curve. Also, for second order kinetics the graph between the reciprocal of the concentration vs time comes out to be a straight graph with positive slope.
Given that:- 1/[A] vs. time is linear which means it follows second order kinetics.
Thus,
Given that slope = k = 0.056 M⁻¹ s⁻¹.
Integrated rate law for second order kinetic is:
![(1)/([A_t]) = (1)/([A]_0)+kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bj32u0ycxy039bxo2npb8w4kujg1ya1aj4.png)
Where,
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c6se0yk0a5jz0ud2m1a9jh5tv0rk9jx59i.png) is the final concentration = Half of the initial concentration = 0.80 /2 M = 0.40 M
is the final concentration = Half of the initial concentration = 0.80 /2 M = 0.40 M
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/i49y9xugeve1tuhjmf05tpufcmfey5f0yu.png) is the initial concentration = 0.80 M
is the initial concentration = 0.80 M
So,
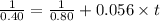
t = 22.32 s