Answer : The equilibrium will shift in the left direction.
Explanation :
Le-Chatelier's principle : This principle states that if any change in the variables of the reaction, the equilibrium will shift in the direction to minimize the effect.
The given reaction is:
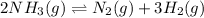
As per question, when we are adding
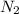 then the concentration of
then the concentration of
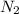 is increased on product side then the equilibrium will shift in the direction where decrease of concentration of
is increased on product side then the equilibrium will shift in the direction where decrease of concentration of
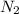 takes place. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift in the left direction.
takes place. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift in the left direction.
Thus, the equilibrium will shift in the left direction.