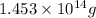This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
Assuming gasoline is 89.0% isooctane, with a density of 0.692 g/mL, what is the theoretical yield (in grams) of CO₂ produced by the combustion of 1.80 × 10¹⁰ gallons of gasoline (the estimated annual consumption of gasoline in the U.S.)?
Answer : The theoretical yield of carbon dioxide is
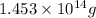
Explanation : Given,
Volume of isooctane =
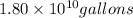
First we have to convert volume into liters, we use the conversion factor:
1 gallon = 3.785 L
So,
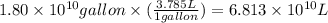
Now we have to calculate the mass of isooctane.
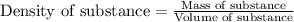
Volume of isooctane =
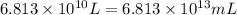 (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
(Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
Density of isooctane = 0.692 g/mL
Now put all the given values in above equation, we get:
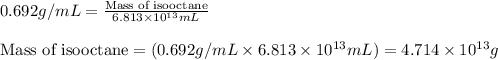
Now we have to calculate the number of moles.
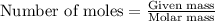 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of isooctane =

Molar mass of isooctane = 114.22 g/mol
Now put all the given values in equation 1, we get:
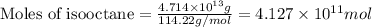
The chemical equation for the combustion of isooctane is:
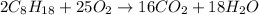
By Stoichiometry of the reaction we can say that,
As, 2 moles of isooctane produces 16 moles of carbon dioxide.
So,
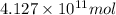 of isooctane will produce =
of isooctane will produce =
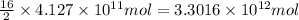 of carbon dioxide
of carbon dioxide
Now we have to calculate the mass of carbon dioxide.
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44.00 g/mol
Moles of carbon dioxide =
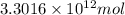
Now put all the given values in equation 1, we get:
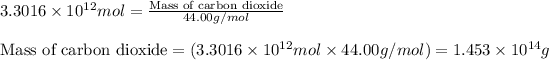
Hence, the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide is