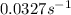Answer : The value of rate constant is,
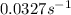
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the rate constant, we use the formula :
Expression for rate law for first order kinetics is given by:
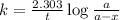
where,
k = rate constant = ?
t = time passed by the sample = 4.84 s
a = initial concentration = 4.17 M
a - x = concentration after time 4.84 s = 3.56 M
Now put all the given values in above equation, we get
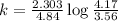
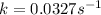
Therefore, the value of rate constant is,