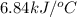This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
A 6.55 g sample of aniline
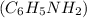 molar mass = 93.13 g/mol) was combusted in a bomb calorimeter. If the temperature rose by 32.9°C, use the information below to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter.
molar mass = 93.13 g/mol) was combusted in a bomb calorimeter. If the temperature rose by 32.9°C, use the information below to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter.
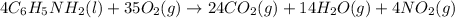
ΔH°rxn = -1.28 × 10⁴ kJ
Answer : The heat capacity of the calorimeter is,
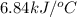
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the moles of aniline.
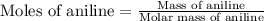
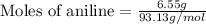
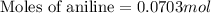
Now we have to calculate the heat releases.
As, 4 mole of aniline on combustion to releases heat =
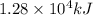
So, 0.0703 mole of aniline on combustion to releases heat =
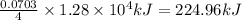
Now we have to calculate the heat capacity of the calorimeter.
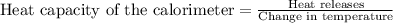
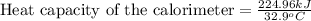
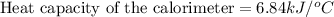
Thus, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is,