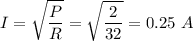Answer:
I = 0.25 A
Step-by-step explanation:
Resistors
The resistors are the circuit elements that oppose the flow of the current. The more resistance an element has, the less current is allowed to go through it. For a resistor of resistance R to which a voltage V is applied, the equation for the current is given by the Ohm's law:
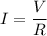
The power dissipated by a resistor R is given by the Joule's law
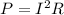
Replacing the first equation into the second, we have
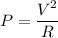
The question refers to a resistor that dissipates P=0.5 W when 4 Volts are applied to it, thus we can compute R solving the above equation for R
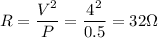
If the voltage is changed such that the new power dissipated by the resistor is 2 W, we can compute the new current, solving the equation of Joule's law for I