Let's recall that, the potential difference between any two points X(x,y,z) and Y(a,b,c) is given by ;
So, here ;
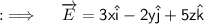
So, now our second component of the Integrand will just be ;
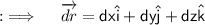
So, now the whole integrand will just be ;
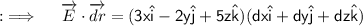
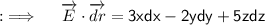
Now, Let's move to the final answer ;
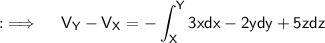
As,X is the point (1,3,5) and Y being (3,2,7) , so seperate the integral into three integrals with limits as follows respectively;
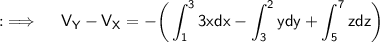
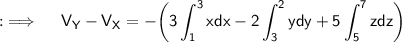
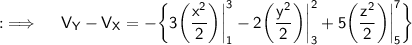
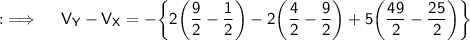
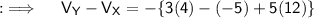
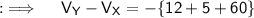
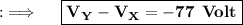
Hence, this is the required answer