Answer:
a)
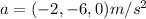 , with a magnitude of
, with a magnitude of
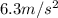
b)
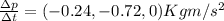 , with a magnitude of
, with a magnitude of
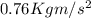
c)
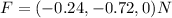 , with a magnitude of
, with a magnitude of
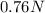
Step-by-step explanation:
We have:
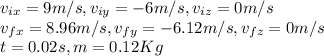
We can calculate each component of the acceleration using its definition
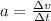
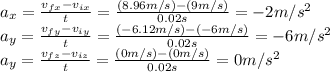
The rate of change of momentum of the ball is
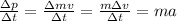
So for each coordinate:
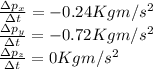
And these are equal to the components of the net force since F=ma.
If magnitudes is what is asked:
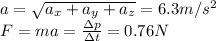
(N and
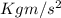 are the same unit).
are the same unit).