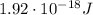Answer:
Electric potential energy at the negative terminal:
Step-by-step explanation:
When a particle with charge
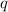 travels across a potential difference
travels across a potential difference
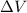 , then its change in electric potential energy is
, then its change in electric potential energy is
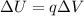
In this problem, we know that:
The particle is an electron, so its charge is
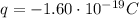
We also know that the positive terminal is at potential
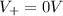
While the negative terminal is at potential
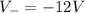
Therefore, the potential difference (final minus initial) is

So, the change in potential energy of the electron is
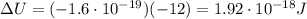
This means that the electron when it is at the negative terminal has
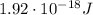 of energy more than when it is at the positive terminal.
of energy more than when it is at the positive terminal.
Since the potential at the positive terminal is 0, this means that the electric potential energy of the electron at the negative end is