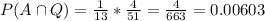Answer:
Explanation:
For this case we assume that we have a total of 52 cards.
We can define the following events:
A|Q= We select an Ace card from the deck given that we select a Quen at the first card
Q = We select a Queen card from the deck for the first selection
We take in count that the experiment is without replacement.
For this case we want to calculate the probability that the second card is an ace, given that the first card is a queen?
So we want to find
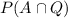
From the bayes rule we know that:
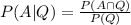
And if we solve for
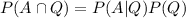
And we can find this probability like this. The probability of select an Queen for the first card is:
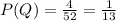
Since we select one card then we have left 51 possible cards in order to select the ace and then we can find:
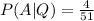
And the probability required would be: