Answer:
Solution with electrolyte will have a lower freezing point than the solution with non electrolyte.
Step-by-step explanation:
Depression in freezing point is given by :
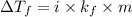
Where :
i = van't Hoff factor
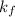 = Molal depression constant of solvent
= Molal depression constant of solvent
m = molaity of the solution
Let the molality of the glucose and NaCl solution be = m
Molal depression constant of water =
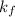
1) The values of van't Hoff factor for glucose is = 1 (non electrolyte)
Depression in freezing point of glucose solution :
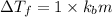
2) The values of van't Hoff factor for NaCl is = 2 (electrolyte)
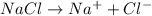
Depression in freezing point of NaCl solution :
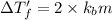
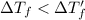
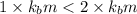
1 < 2
Higher the depression in freezing point more will be the lower freezing point of the solution.This means that solution with electrolyte will have a lower freezing point than the solution with non electrolyte.