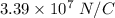Answer:
(a). The charge on the outer surface is −2.43 μC.
(b). The charge on the inner surface is 4.00 μC.
(c). The electric field outside the shell is
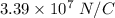
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Charge q₁ = -4.00 μC
Inner radius = 3.13 m
Outer radius = 4.13 cm
Net charge q₂ = -6.43 μC
We need to calculate the charge on the outer surface
Using formula of charge
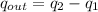
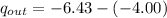
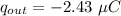
The charge on the inner surface is q.
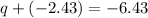
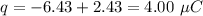
We need to calculate the electric field outside the shell
Using formula of electric field
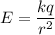
Put the value into the formula
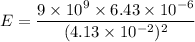
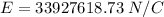

Hence, (a). The charge on the outer surface is −2.43 μC.
(b). The charge on the inner surface is 4.00 μC.
(c). The electric field outside the shell is