Answer: The vapor pressure of solution is 459.17 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
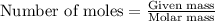 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of testosterone = 7.752 g
Molar mass of testosterone = 288.4 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
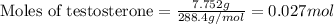
Given mass of diethyl ether = 208.0 g
Molar mass of diethyl ether = 74.12 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
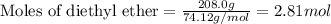
Mole fraction of a substance is calculated by using the equation:
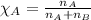

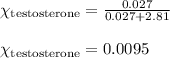
The formula for relative lowering of vapor pressure will be:
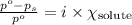
where,
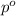 = vapor pressure of solvent (diethyl ether) = 463.57 mmHg
= vapor pressure of solvent (diethyl ether) = 463.57 mmHg
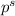 = vapor pressure of the solution = ?
= vapor pressure of the solution = ?
i = Van't Hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolytes)
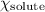 = mole fraction of solute (testosterone) = 0.0095
= mole fraction of solute (testosterone) = 0.0095
Putting values in above equation, we get:
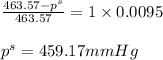
Hence, the vapor pressure of solution is 459.17 mmHg