x = 5
Solution:
Given equation is
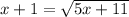 .
.
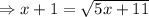
Squaring on both sides of the equation to remove the square root.
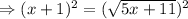
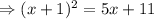
Using algebraic identity:
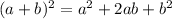
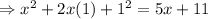
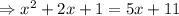
Combine all terms in one side of the equation.
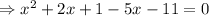
Arrange like terms together.
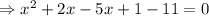
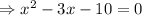
Now solve by factorization.
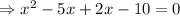
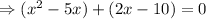
Take common terms on left side of the term.
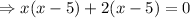
Now, take (x – 5) common on both terms.
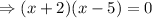
⇒ x + 2 = 0 (or) x – 5 = 0
⇒ x = –2 (or) x = 5
If we put x = –2 in the given equation,
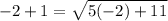
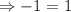
It is false. So, x = –2 is not true.
If we put x = 5 in the given equation,
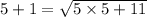
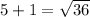
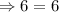
It is true. So, x = 5 is true.
Hence x = 5 is the solution.