Answer:
BOYLE'S Law
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of a fixed quantity of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas.
Mathematically:
From the universal gas law we have:
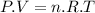
where:
P = pressure of the gas
V = volume of the gas
n = no. of moles of gas
T = temperature of the gas
R = universal gas constant
when the mass of gas is fixed i.e. n is constant and temperature is also constant.
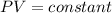
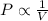
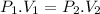
here the suffix 1 and 2 denote two different conditions of the same gas.