Answer:
Decreases
Step-by-step explanation:
Gauss's law states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the quotient between the charge inside that surface divided by the permittivity of free space:
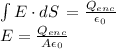
Therefore, the magnitude of the electric field is inversely proportional to the area, the area is directly proportional to the radius. So, as the radius of the Gaussian surface increases, the magnitude of the electric field at the surface decreases.