Step-by-step explanation:
Henry's law states that the amount of gas dissolved or molar solubility of gas is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the liquid.
To calculate the molar solubility, we use the equation given by Henry's law, which is:
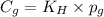
where,
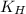 = Henry's constant
= Henry's constant
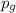 = partial pressure of gas
= partial pressure of gas
A.
Henry constant =
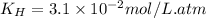
Pressure of the carbon dioxide gas in an unopened bottle:
=
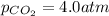
Putting values in above equation, we get:
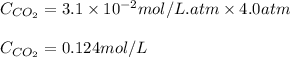
0.124 mol/L is the solubility of
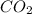 gas-in-an-unopened soft drink bottle.
gas-in-an-unopened soft drink bottle.
B.
Molarity of
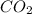 gas = 0.124 mol/L
gas = 0.124 mol/L
Moles of
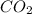 gas in 2 Liter of soft drink:
gas in 2 Liter of soft drink:
= 0.124 mol/L × 2 L = 0.248 mol
0.248 moles of
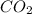 gas are dissolved in an unopened 2 liter soft drink bottle.
gas are dissolved in an unopened 2 liter soft drink bottle.
C.
Pressure at sea level = P = 1 atm
Mole fraction carbon dioxide gas at sea level:
=
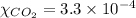
So, partial pressure of the
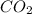 gas :
gas :
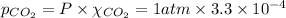
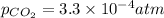
Henry constant =
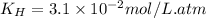
The solubility of
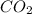 gas in the opened soft drink at sea level:
gas in the opened soft drink at sea level:
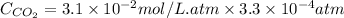
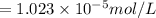
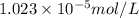 is the solubility of
is the solubility of
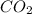 gas in opened soft drink bottle at sea level.
gas in opened soft drink bottle at sea level.
D.
Molarity of
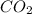 gas in opened soft drink bottle at sea level =
gas in opened soft drink bottle at sea level =
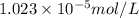
Moles of
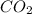 gas in 2 Liter of soft drink left open at sea level?:
gas in 2 Liter of soft drink left open at sea level?:
=
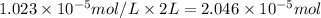
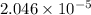 moles of [tex]CO_2[tex] gas are dissolved in 2 liter soft drink left open at sea level?
moles of [tex]CO_2[tex] gas are dissolved in 2 liter soft drink left open at sea level?